Activation of the UNC Site
Activation at UNC is complex involving several departments and many functional groups within those departments.
There are four main types of clinical trials comprising our portfolio, all of which have different activation principles:
- Investigator initiated trials (IITs) that have an investigational new drug application (IND)
- IITs that are IND exempt
- National Cancer Institute (NCI) study approved by NCI’s central Institutional Review Board IRB (NCI CIRB)
- Pharmaceutical sponsored clinical trials
Who is There to Help Me with Activation in the Clinical Trials Office (CTO)?
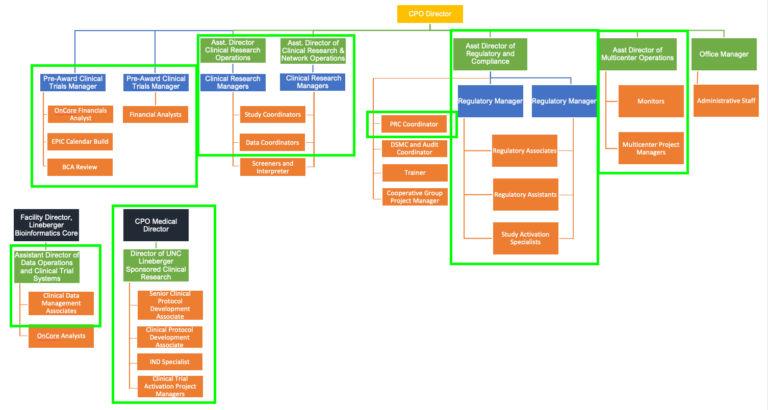
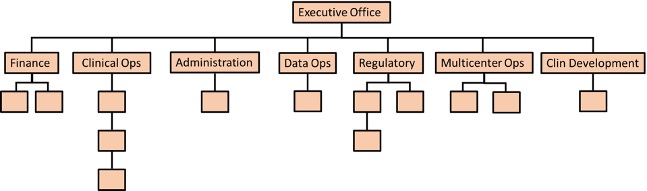
Activation includes the vast majority of the CTO and many other groups within UNC. Although the below organizational chart may change over time by titles and/or reporting lines, the key thing to note is just how much of the office has a role in activation (green lined boxes):
Click to expand image
Who are the CTO players who are involved in activation of all studies?
The following individuals within the CTO help with activation of all types of clinical trials. Please refer to the “Activation 101 – Who are the Players” training to learn more about each of their roles.
Pre-Award Finance Manager- Oversees all calendar build tasks in OnCore
- Works with the Office of Clinical Trials (OCT) and Billing Coverage Analysis (BCA) Analyst to ensure the BCA is built as needed in OnCore
- Oversees the OnCore Financials Analyst, Financial Analysts, EPIC Calendar Build and BCA Review
- Trains financial analysts and develops standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- Works with other members of the activation team to ensure CTO is meeting its goals
- Oversees the financial analysts
- Works with OnCore India on calendar builds
- Enters all financials and coverage analysis
- Builds items within the calendar – procedures, prices, and identifies pass-through items
- Ensures amendments are reflected in OnCore
- Build Epic billing calendars for all oncology trials
- Validates and imports OnCore calendars/adds treatment levels
- Enters service now ticket to initiate a Beacon build
- Negotiates the budget
- Works with OCT on BCAs
- Processes Amendments
- Coordinates with the contracts team
- Registers the study in OnCore
- Submits to the Protocol Review Committee (PRC) (for all studies but IITs)
- Submits to other institutional committees, as required (Institutional Biosafety Committee [IBC]), Radiation Safety, Investigational Drug Services [IDS])
- Completes Initial IRB submissions
- Drafts the informed consent form from the sponsor template and gains sponsor approval of the consent form
- Processes the IRB submission in OnCore (uploading all of the documents such as the IRB approval, lab manual, electronic case report form (eCRF) guidelines)
- Collects staff training
- Preparation of essential regulatory documents (e.g., Form Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 1572, financial disclosures, protocol signature page)
- Develops the flow sheet
- Aids the PI in selecting studies
- Ensures operations are ready to open the study (e.g., securing kits, ECG machines, EDC access, IXRS system access, central lab manager access)
- Sets up an account with the Tissue Procurement Facility (TPF)
- Sets up access with the radiology core
- Leads the start-up meeting
- Selects the study
- Advocates for timely activation
- Introduces the team to the trial during the start-up meeting
- Approves/Signs Off on:
- Institutional Review Board (IRB) application
- Informed consent form (ICF) language
- Billing Coverage Analysis (BCA)
- Clinical Trial Agreement (CTA) (the contract)
- FDA submission (if an IIT)
- eCRFs (if an IIT)
Who are the players within UNC who help with all clinical trial activation?
The following individuals within the UNC and external to the CTO help with activation of all types of clinical trials. Please refer to the “Activation 101 – Who are the Players” training to learn more about each of their roles.
Beacon CoordinatorBeacon Oncology Information System is the oncology module of EPIC. Within Beacon the treatment plans (drug assignments) are developed for each protocol. These plans include study procedures and standard orders for supportive care. Additional protocol specific timepoints can also be built to be accessed by all oncology care team members. The Beacon Coordinator is in charge of creating this build.
Creates IDS Information Sheet on how the drug must be prepared, key protocol information, etc.
- Acquire access to the sponsor drug systems
- Order required supplies
- Validate the Beacon Build
- Receive the study drug
- Complete the BCA
- Perform a compliance check (comparison of the BCA, CTA, and IRB approved ICF)
- Review/Approve ICF injury language
- Industry contracting
- Negotiate the CTA
- Negotiate Confidentiality Disclosure Agreements (CDAs) and Data Use Agreements (DUAs) for all trials
- Negotiate Subcontractor Agreements (e.g., drug distribution entities, multicenter sites, correlative analysis)
- Perform proposal (grant) review and submission
- Negotiate awards
- Generate and release the Chartfield String (account #)
What committees are involved in activation?
- Protocol Review Committee (PRC) provide peer review of the protocol ensuring scientific quality and patient safety of the proposed studies
- Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) reviews gene therapy protocols to mitigate risks to human health, the environment and public health
- Radiation Safety Committee (RSC) review studies using more radiation than is administered via standard of care (e.g., more frequent CT scans) and provides ICF risk language for the use of this excess radiation
- Institutional Review Board (IRB) ensure ethical and regulatory oversight of research focusing on rights and welfare of human research subjects and the ethical conduct of all research involving human subject
What additional groups are involved in the activation of IITs?
IND Specialist- Completes FDA submissions
- Drafts Informed Consent Form templates
- Drafts patient handouts
- Submit Letters of Intent (LOIs)
- Aid in the development of initial study budgets
- Aid in the development of the clinical protocol
- Lead protocol review meetings and correlative review meetings
- Develop the data management plan (DMP) & identify critical data values (CDVs)
- Build subject calendars
- Develop eCRFs
- Completes the ClinicalTrials.gov registration
- Develop the study-specific monitoring plan
What additional groups are involved in the activation of multicenter IITs?
Multicenter Project Managers (PMs)- Help PI identify sites
- Initiate the CDA process with the sites
- Develop a feasibility questionnaire to aid in site selection
- Initiate budget discussions with the sites
- Ensure regulatory activities at the sites (such as IRB submissions) are ongoing
- Process the site contracts
- Lead site initiation meetings (SIMs)
- Provide study documents to the sites
- Collect IRB and other local approvals of the study documents
- Collect the site’s essential regulatory documents (e.g., Form FDA 1572)
What is the role of the Clinical Trial Activation Project Manager?
The Clinical Trial Activation PM completes the following tasks:
- Project Manages activation:
- Schedules activities and completion dates
- Monitors the progress of activation using Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) charts (see below)
- Allowed slack times
- Critical path deliverables
- Key milestone deadlines
- Identifies hurdles to progress and helps the study team overcome those hurdles
- Communicates with stakeholders
- Leads, coaches, motivates, and influences assigned study team members to ensure timely completion of high-quality deliverables and staff accountability
- Tracks trends and analyzes data regarding pitfalls to activation
- Proposes initiative to address activation hurdles
To learn more about their role please check out “Activation 201 – What is the Role of the Activation PM”
Principles behind the Activation Processes
We use business principles of critical paths and Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) charts to determine the fastest way to open your clinical trial involving these many departments. Our Clinical Trial Activation Project Managers ensure all departments and functional groups are synchronized in this effort.
What is a Critical Path and PERT Chart?
A critical path is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is determined by the following:
- Identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities
- Measuring the time required to complete the activities from start to finish
A PERT chart is a visual representation of these dependent activities, the critical path, and the timelines it takes to complete each of the dependent activities. Please also refer to the talk: “What is a “Critical Path” and How Can it Help Me?” for additional training.
So instead of thinking of all tasks as a linear list, such as this:
![]()
Tasks are arranged by what tasks must be completed prior to the next task being completed (their dependencies):
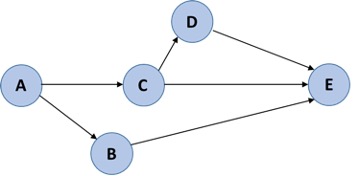
In the above example, A must occur before B and C, but you don’t need to complete B to move on to C. Instead, B and C may be completed at the same time.
After the tasks are arranged by dependencies, you determine the amount of time each dependent step takes and figure out the longest path from starting a task until its completion (A-E above). This is referred to as the critical path and is highlighted in our example below in red.
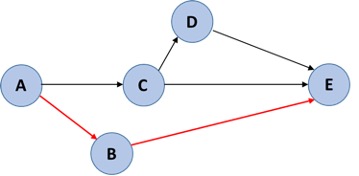
From this you then know what tasks are most important to be done immediately and how much extra time you have to perform tasks not on the critical path (your lag time).
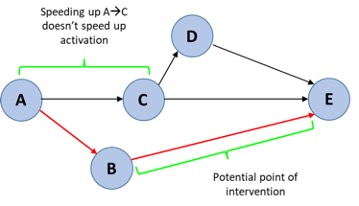
If you want to speed up activation and make it more efficient, only speeding up tasks on the critical path will reduce timelines since they overall take the longest:
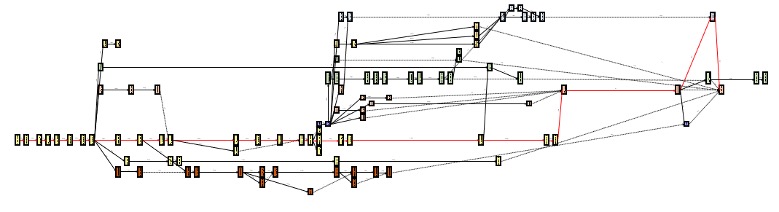
What do LCCC CTO’s Activation PERT Charts look like?
In addition to the below, please refer to the talk “Project Management of Activation” for additional explanation/training.
Below is an example of a PERT chart for an IIT, which has an IND. Each functional group is represented by a different color.
What is Project Management?
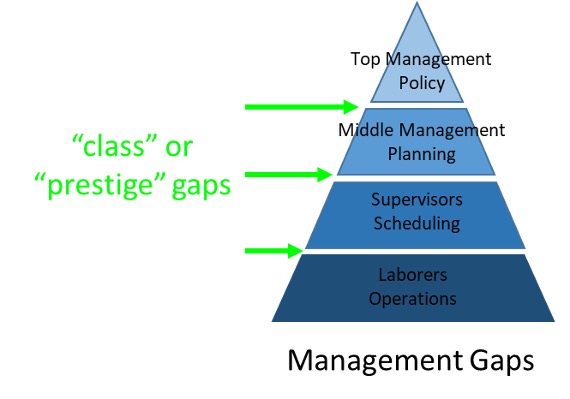
Many organizations including ours is made up of a traditional organizational structure:
Traditional organization structures lead to operational islands, which are created by organizational gaps. First, there are gaps between different levels of management (class or prestige gaps):
There are also functional gaps between different working units of the organization or departmentalization:
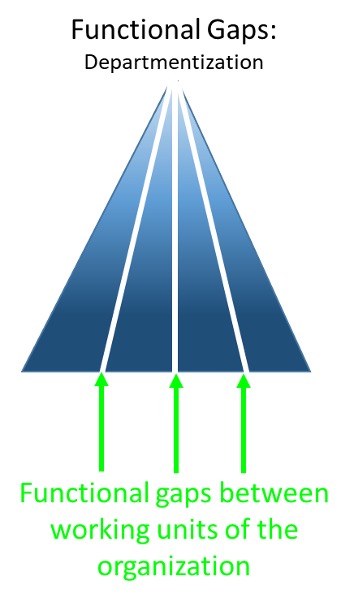
When these are overlapped with one another they form operational islands.
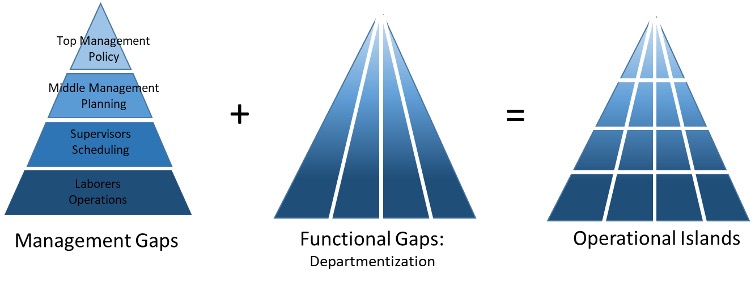
These “islands” refuse to communicate with one another for fear that giving up information that may “strengthen” their opponents.
Project management is designed to make better use of existing resources by getting work and communication to both both horizontally and vertically within a company. They aid everyone in contributing to common goals and objectives. In other words, a combination of the line manager and and the project manager fill the gaps which form the operational islands:
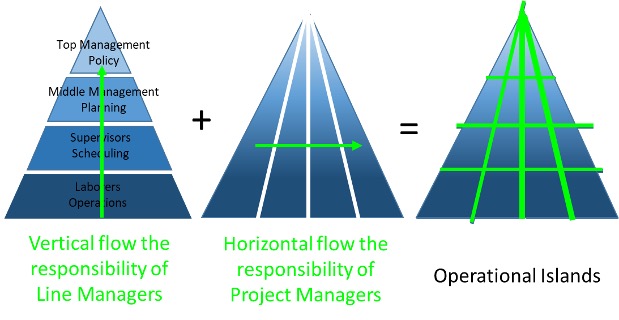
Project management is in charge of 4 major resources to help in accomplishing goals:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Directing
- Controlling
References
Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling and Controlling, 10th Edition by Harold Kerzner (ISBN: 978-0-470-27870-3)