Research

Our lab focuses on developing new and exciting approaches for enhancing the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies.
We utilize cutting-edge genomics, bioengineering, computational, and immunological techniques to identify molecular drivers of T cell differentiation and function in the tumor microenvironment. Our ultimate goal is to devise effective strategies for reprogramming or tailoring the activity of T cells in cancer.
Our group is also interested in understanding how to harness or manipulate T cell responses to improve vaccines and immunotherapies for acute and chronic infections. The Milner Lab is located at the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center in Chapel Hill, NC.
Molecular regulation of T cell activity in the tumor microenvironment
Harnessing the protective capacity of the immune system to eliminate malignant cells has emerged as an exciting and promising strategy for the treatment of cancer. A primary focus of our lab is to develop new approaches for enhancing the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies. Promising modalities in the immuno-oncology landscape include checkpoint blockade, adoptive cell therapy, cancer vaccines, cytokine therapies, and oncolytic viruses (Figure 1).
Cytotoxic CD8 T lymphocytes play a fundamental role in cancer immunity with a unique ability to directly target and kill tumor cells, and as such, the success of most immunotherapies hinges on the quality and robustness of the anti-tumor CD8 T cell response. However, inhibitory features of the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment often prevent sustained T cell activity and efficient elimination of malignant cells, contributing to variable immunotherapy responsiveness and treatment resistance.
We use single-cell genomics, computational methods, bioengineering approaches, and immunological techniques to delineate the complex signals regulating tumor-specific CD8 T cell fate, heterogeneity, persistence, and function in cancer (see Figure 2 in collaboration with Dr. Natalie Stanley). We aim to strategically reprogram the activity of T cells in cancer through manipulating the activity of key transcription factors and epigenetic regulators.
High-throughput screens in the immune system
We are developing new screening strategies to rapidly define complex signals controlling immune responses in the tumor microenvironment. Through collaborations with Dr. Natalie Stanley and other fantastic investigators at UNC, we are implementing a multi-disciplinary approach that integrates genetic screens and single-cell omics to uncover new strategies for fine-tuning immune responses in vivo.
Modulating T cell differentiation in response to infection and vaccination
Our group also studies the molecular signals controlling T cell differentiation and function in response to infection or vaccination. Memory CD8 T cells provide long-lived protection against pathogens. However, the mechanisms controlling their formation and function remain unclear, and our ability to therapeutically enhance memory T cell responses remains limited. We are interested in identifying fate-specifying signals controlling memory T cell differentiation and heterogeneity (Figure 3), with a particular focus on tissue-resident memory cells that surveil barrier tissues such as the intestine and respiratory tract.
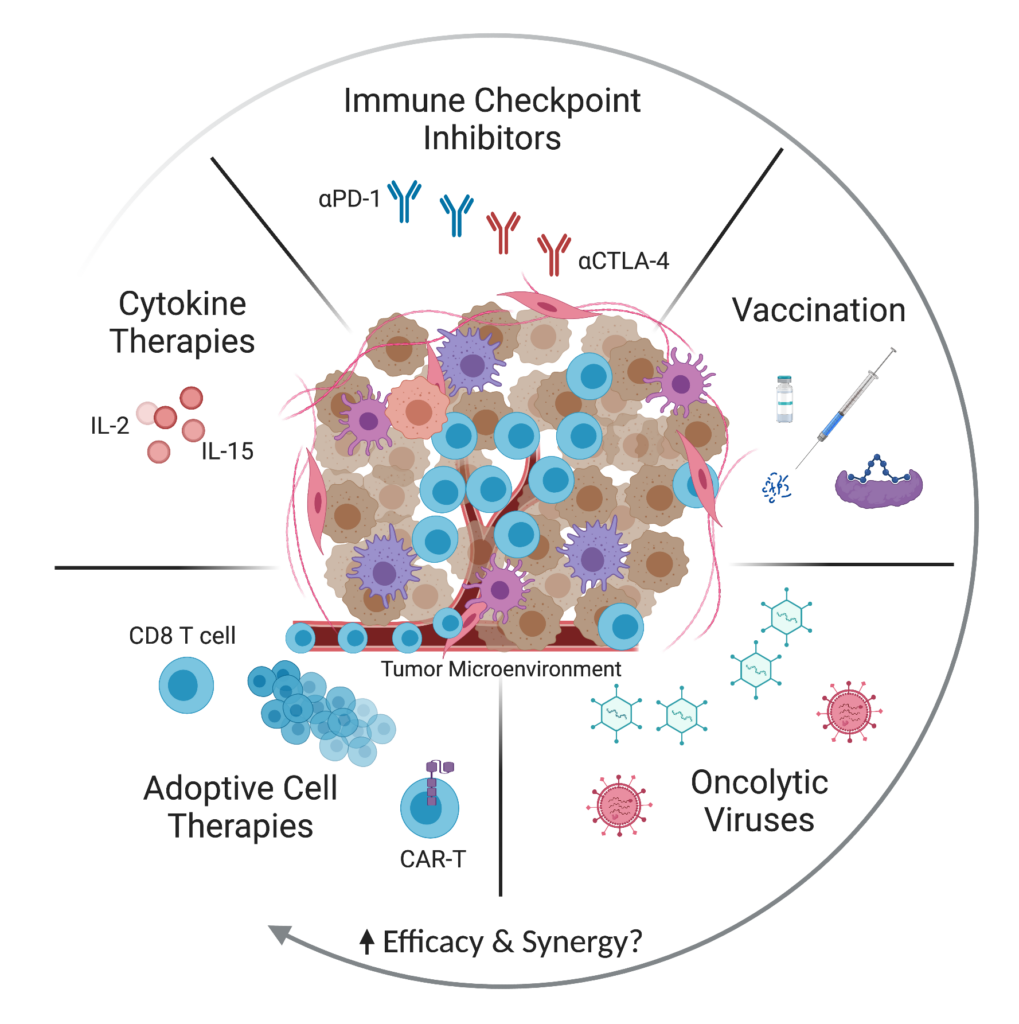 Figure 1
Figure 1
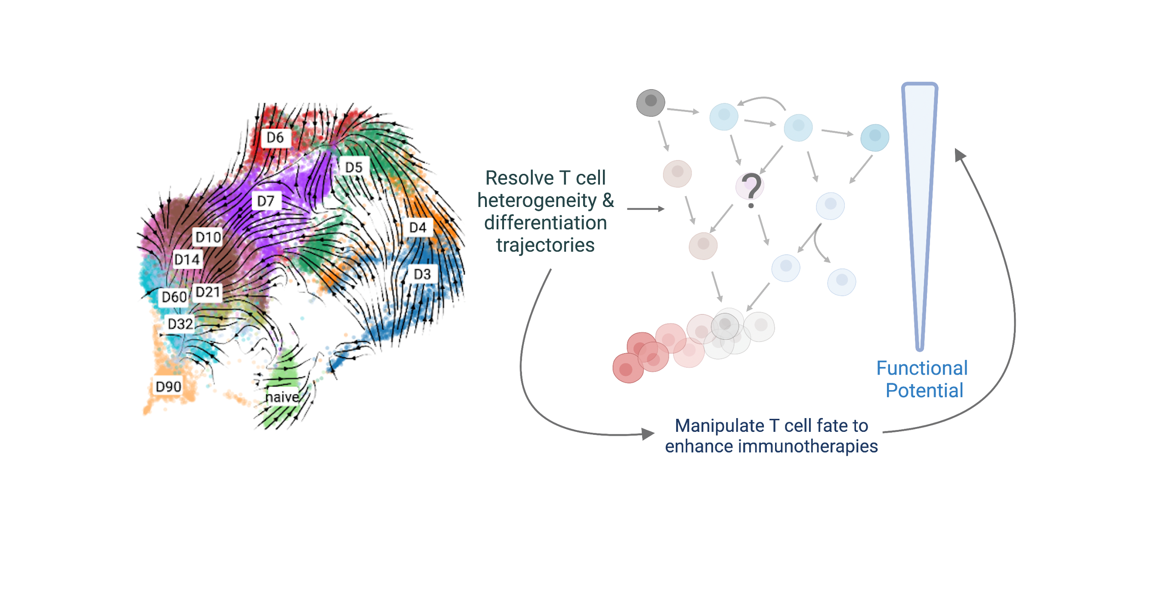 Figure 2
Figure 2
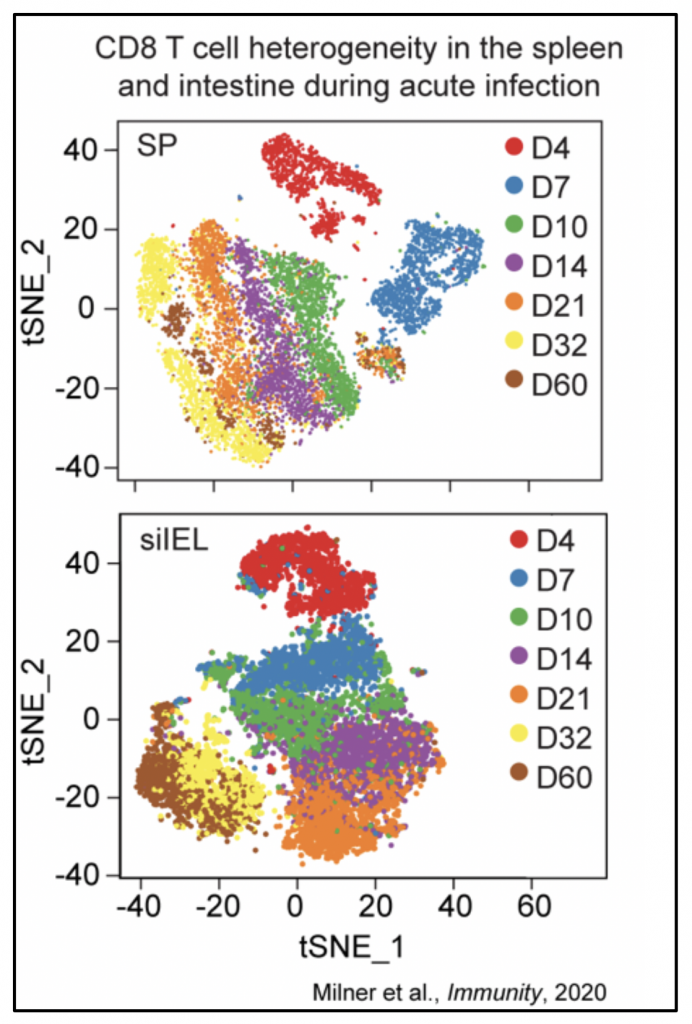 Figure 3
Figure 3
Figure 1 was generated with Biorender.com